
Plastics and Microplastics: A Threat to the Environment and Health
EHHI reviewed nearly 500 scientific studies for this report and found that each of us ingests and inhales millions of microscopic plastic particles each year. Microplastics carry chemical additives and coatings as well as potentially pathogenic microbes. Disturbingly, their impact on human health is not yet known.
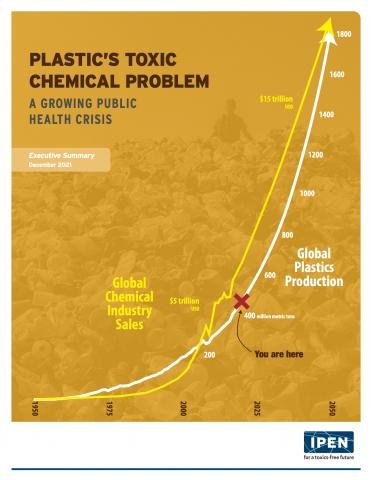
Plastic’s Toxic Chemical Problem: A Growing Public Health Crisis
IPEN and IPW studies show that throughout their life cycle, plastics transport and release toxic chemicals globally, posing serious threats to human health and ecosystems.

A Rapid Review and Meta-regression Analyses of the Toxicological Impacts of Microplastic Exposure in Human Cells
The prevalence of microplastics (MPs) is ubiquitous, found in almost every compartment of the environment; in the air (Wright et al., 2020), food (Teng et al., 2019) and drinking water (Zhang et al., 2020). MP contamination will continue to rise as plastic production and use around the world increases (Lebreton and Andrady, 2019). If plastic waste mismanagement continues as it is or increases, it is predicted that within a century, MP ecological risks will be widespread in ecosystems across the world (SAM, 2019; SAPEA, 2019).

Plastic Waste Poisoning People in Africa, Asia, Central and Eastern Europe & Latin America
Plastics and food packaging contain chemical contaminants from manufacturing along with many additives to make them inflammable, more flexible, grease-resistant, or sterile, as well as other substances to create many other properties. Many of these additives are toxic and they leak from products during use and can be released during recycling and from recycled products.
This study focuses on persistent organic pollutants (POPs), whose releases are closely related to plastic wastes. The POPs include additives in the plastic as such, as well as unintentionally produced POPs (UPOPs) generated mostly by burning, incineration and/or other thermal treatment of plastics.
Four samples from this study are among the ten highest ever measured levels of chlorinated dioxins in chicken eggs globally.

Deep Dive into Plastic Monomers, Additives, and Processing Aids
A new study finds that plastics release many more toxic chemicals throughout their life cycle than previously thought, posing significant risks to both people and the planet.

Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue
Microplastics are present in the air and may be inhaled by humans, but whether they have deleterious effects on the respiratory system remain unknown. In this study, we determined the presence of microplastics in human lung tissues obtained at autopsies.

Are Bioplastics and Plant-Based Materials Safer Than Conventional Plastics? In Vitro Toxicity and Chemical Composition
Plastics contain a complex mixture of known and unknown chemicals; some of which can be toxic. Bioplastics and plant-based materials are marketed as sustainable alternative to conventional plastics. However, little is known with regard to the chemicals they contain and the safety of these compounds. Thus, we extracted 43 everyday bio-based and/or biodegradable products as well as their precursors, covering mostly food contact materials made of nine material types, and characterized these extracts using in vitro bioassays and non-target high-resolution mass spectrometry.

