
Black-colored plastic used for kitchen utensils and toys linked to banned toxic flame retardants
Black-colored plastic used in children’s toys, takeout containers, kitchen utensils and grocery meat and produce trays may contain alarming levels of toxic flame retardants that may be leaching from electronic products during recycling, a new study found.
Plastics producers are following Big Tobacco’s playbook, and we’re all paying the price
Let’s not fall for another false solution offered by companies to maintain their profit margins. Let’s not allow chemical recycling to win with the same deceptive playbook used by Big Tobacco. We need real change now — and it can’t begin until companies are required by new laws to break their plastic habit and give consumers safe packaged products that don’t threaten the health of people or the planet.

Microplastics Are in Our Food, Too. How Worried Should We Be?
Of course, you’re not going to avoid microplastic consumption by shunning protein. According to Melissa Valliant, communications director for the nonprofit Beyond Plastics, microplastics have also been found in milk, fruits, vegetables, sugar, salt, honey—basically anything that’s been studied.

Toxic Plastic Chemicals Number in the Thousands, Most Are Unregulated, Report Finds
“Life in plastic; it’s fantastic,” so the song goes, but in reality, plastics and the chemicals used to create them have been increasingly linked to numerous harms to human health and the environment. And with new plastic chemicals entering the market all the time, it’s been difficult for regulators and policy makers to determine the scope of the problem. Now, for the first time, researchers have pulled together scientific and regulatory data to develop a database of all known chemicals used in plastic production.
What Does Plastic Do to the Endocrine System?
Before this plastic enters the natural ecosystem, the chemicals inside can leach out of water bottles and other food containers, entering the body and potentially endangering human health, according to a mounting body of research. In particular, plastic contains endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) that could wreak havoc on certain messaging systems in the human body.
America Is Replacing Its Pipes: Is Ductile Iron Pipe a Good Alternative for Plastic?
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), there are 240,000 water main breaks each year and over the next two decades, it’ll take about $420 billion to repair and improve the nation’s water distribution and transmission systems. In addition to aging pipes there are those that pose clear health risks: In 2021, Congress allocated $15 billion specifically for replacing lead service lines. The decision that municipalities across the country will face now is what type of pipe material they should use to replace the old ones.

Plastics Are Fossil Fuel Industry’s Plan B. Fenceline Communities Pay the Price.
Just this past January, new studies found huge numbers of plastic particles in bottled water and microplastics in nearly 90 percent of sampled proteins like beef and tofu. These reports follow many others that have found microplastics and nanoplastics in nearly every crevice of our world: clouds and rivers, Arctic sea ice and sea mammals, heart tissue and breast milk and even placentas.

A Plastic Chemical Caused a Toxic Mess in Ohio Last Year. Now, the EPA Is Eyeing Regulation.
The EPA announced last month that it’s launching a 12-month evaluation period for five hazardous plastic- and petrochemical-related substances, including vinyl chloride. It’s the first step in a potentially yearslong process that could lead to a nationwide ban.

‘I Feel Like I Don’t Matter’: East Palestine Waits for a Presidential Visit
When Jessica Conard heard that President Biden would visit her community in East Palestine, she felt a sense of relief. Mr. Biden’s presence, she believed, would signal to the world that nothing short of disaster happened here in February, when a Norfolk Southern train skipped the tracks and spilled thousands of gallons of toxic chemicals into the environment. All these months later, she’s still waiting for him.
EPA begins formal review of 5 toxic chemicals, including one in Ohio train derailment
The U.S. Environmental Agency Thursday took the first step toward potentially restricting or banning the use of five toxic chemicals used to make plastics, adhesives and paints. Among them is a key ingredient in PVC plastic – vinyl chloride – a common material for water and sewer pipes, medical equipment and toys. It’s also a known carcinogen, and exposure to the substance has been linked to numerous health effects.

US Begins Review That Could Eventually Lead To PVC Ban
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on Thursday announced a review that could eventually lead to the end of PVC plastic production -- impacting everything from records to rubber ducks. Vinyl chloride, which is used in the manufacturing and processing of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), was officially classified as a human carcinogen in 1974 and banned in hair sprays, refrigerants, cosmetics and drugs.

EPA takes first step to review safety of chemical in East Palestine crash
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) began the review process for vinyl chloride, the toxic substance that spilled in the town of East Palestine, Ohio, in February, in the first step toward further restrictions or a potential ban.

EPA goes after plastics with chemicals plan
EPA announced it is prioritizing risk evaluations for five chemicals primarily used to make plastics, signaling a growing and concerted effort to crack down on plastics. Wednesday’s announcement marks the start of a 12-month process that EPA said will likely result in each chemical’s designation as a “high priority” substance under the Toxic Substances Control Act. With that designation, regulators can then launch the intensive, 3 ½-year review process that could lead to the agency banning or restricting uses of the chemical if deemed unsafe.
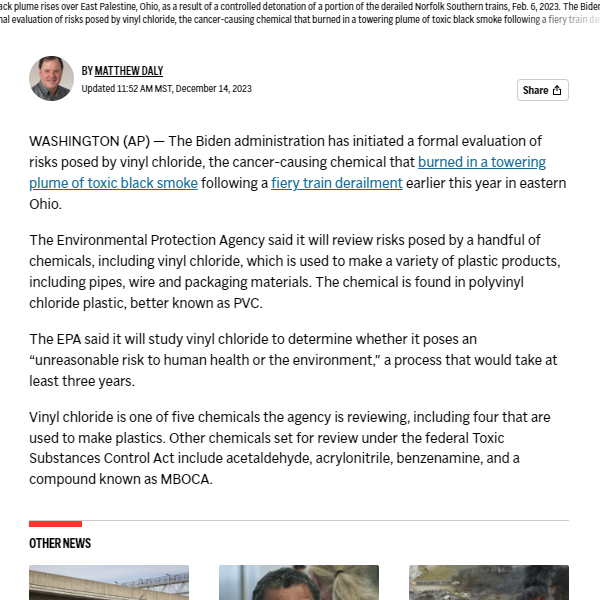
EPA begins formal review of vinyl chloride, toxic chemical that burned in Ohio train derailment
The Biden administration has initiated a formal evaluation of risks posed by vinyl chloride, the cancer-causing chemical that burned in a towering plume of toxic black smoke following a fiery train derailment earlier this year in eastern Ohio.
Judith Enck: Chicago must choose lead pipe replacement material carefully
I applaud the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s decision to mandate the removal of lead pipes used for drinking water nationwide. A Michigan State University professor and pediatrician was widely quoted in recent articles saying, “This is like a pediatrician’s dream come true.” But the Biden administration must ensure that we don’t swap one problematic material for another. Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, pipes will undoubtedly be considered as a replacement for lead pipes in Chicago and elsewhere, and they come with their own serious concerns.

Microplastics Pose Risk to Ocean Plankton, Climate, Other Key Earth Systems
An estimated 12 million metric tons of plastic currently enters the ocean each year. This plastic debris gradually breaks down into smaller and smaller fragments — micro- and nanoplastics — which, while less visually striking, can have serious effects on marine ecosystems and may even pose a threat to the stability of Earth’s climate. A recent estimate suggests that as much as 358 trillion microplastic particles are floating on the surface of the world’s oceans, with untold trillions more in deeper reaches.

Dark Plastics
If your home has HDPE plastic containers— it almost certainly does; look for the No. 2—you should know some of it may have been treated with a process called fluorination. And you might be exposing yourself to PFAS, the “forever chemicals.”
EPA Approved a Fuel Ingredient Even Though It Could Cause Cancer in Virtually Every Person Exposed
The Environmental Protection Agency approved a component of boat fuel made from discarded plastic that the agency’s own risk formula determined was so hazardous, everyone exposed to the substance continually over a lifetime would be expected to develop cancer. Current and former EPA scientists said that threat level is unheard of. It is a million times higher than what the agency usually considers acceptable for new chemicals and six times worse than the risk of lung cancer from a lifetime of smoking.
President Biden, Come to East Palestine and Bring FEMA With You
The Ohio train derailment is not a comeback story, it's a grim warning. It's about an industry that values profit over people and the environment, and about a regulatory system that has failed to keep these industries in check. There is an undeniable connection between this disaster and the plastics industry. The production of PVC plastic depends on transporting harmful chemicals like vinyl chloride. The insatiable demand for plastics has driven the need for increased transport of these hazardous substances, placing communities near rail tracks under constant threat. As company profits soar, our communities are left to grapple with the aftermath of their negligence.
Plastic's Health Impacts Are Becoming Impossible To Ignore
Plastic has been creeping into our food, our air, our water, and our bodies for decades now, with most people blissfully unaware of its presence and health risks. But two catastrophes in the past six months suddenly made it impossible to ignore how plastic affects Americans' lives, health, and future. The catastrophes I'm referring to are the East Palestine, Ohio, train derailment and the smoke from Canadian wildfires that enveloped U.S. cities for days. If you're not already aware—and many aren't—these two moments have everything to do with plastic. Let me explain.

